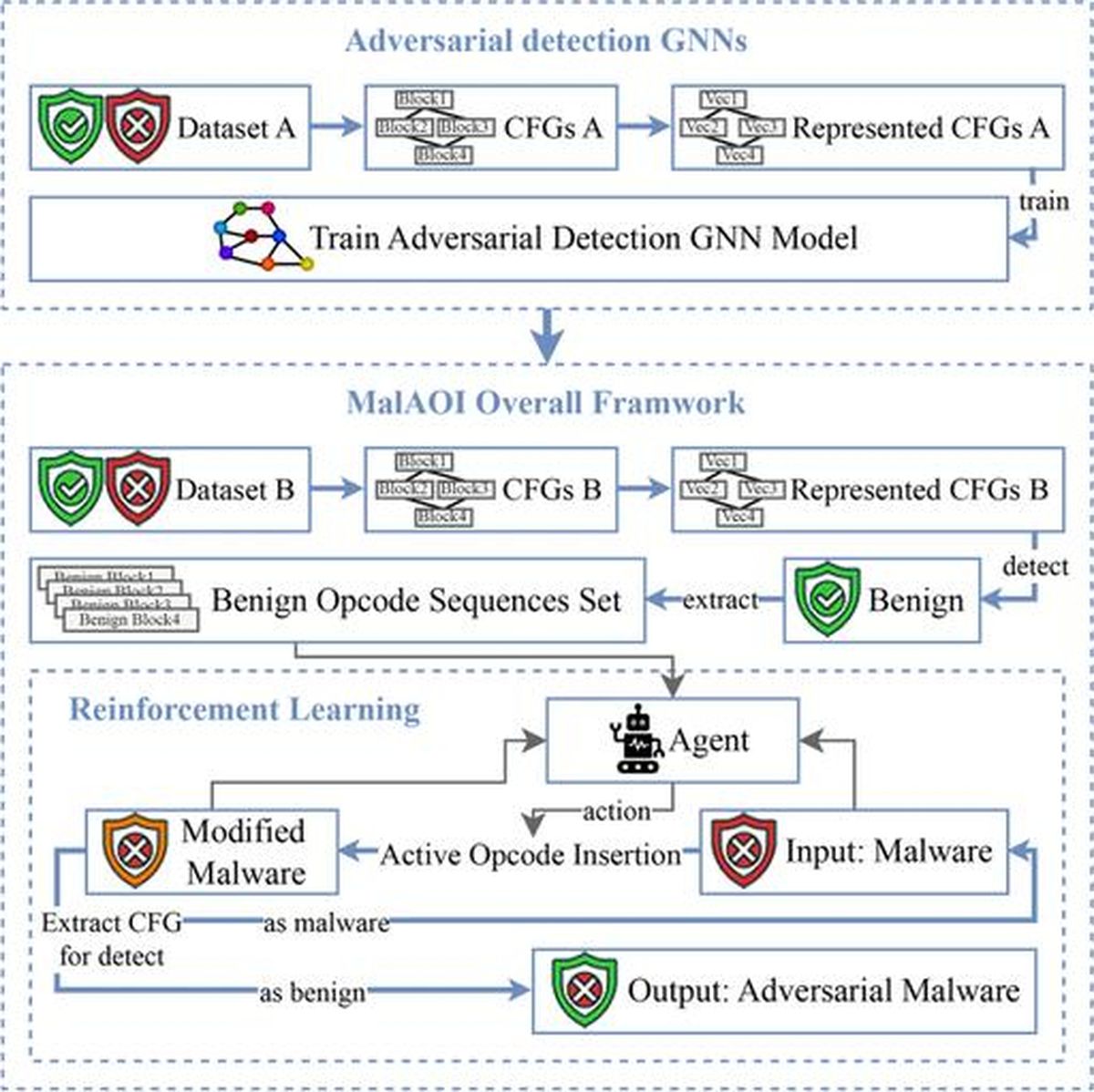
Innovative techniques based on machine learning are leading advances in malware detection. A recent study introduces an active opcode insertion technique utilising reinforcement learning, allowing malware to evade detection by graph neural network (GNN) models. The system, called MalAOI, modifies malware control flow graphs while retaining functionality. Tests demonstrated a 93.73% evasion rate against GNN detection, revealing vulnerabilities in existing systems while also highlighting potential areas for future cybersecurity research and development.
NIST Releases Reference Material to Aid Gut Microbiome Research
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) has launched a stool reference material to help researchers measure the gut microbiome more accurately. The “Human